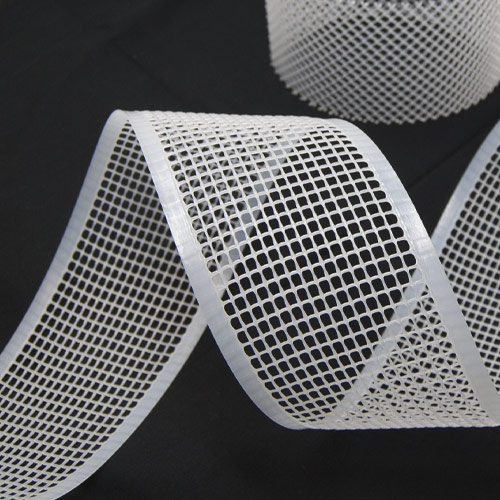
Filtration & Separation
A wide range of applications
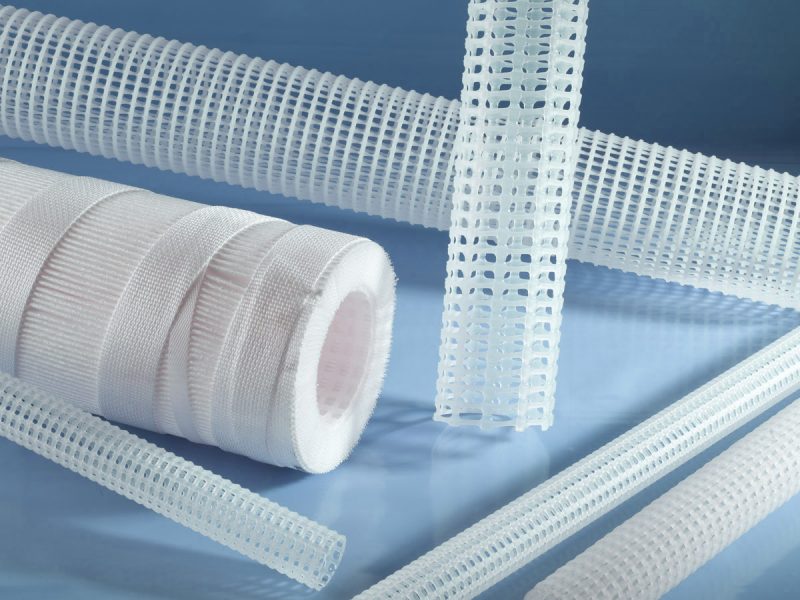
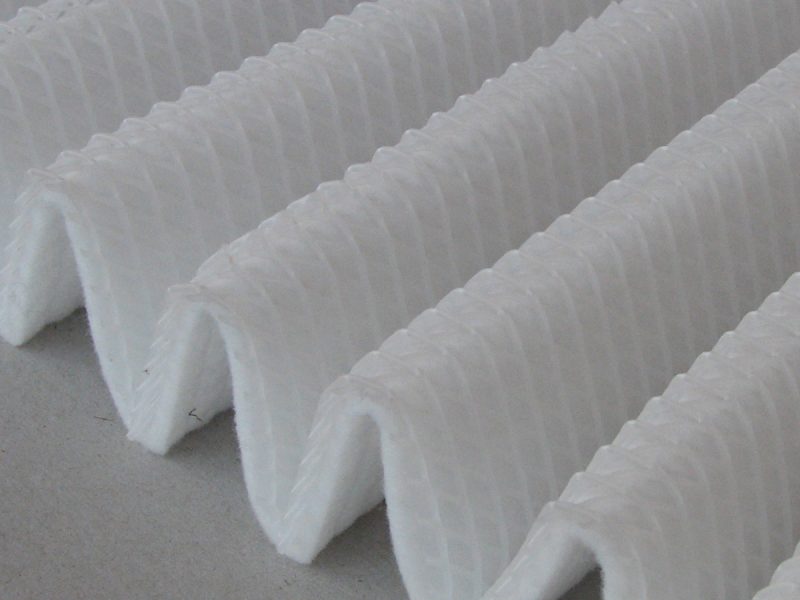
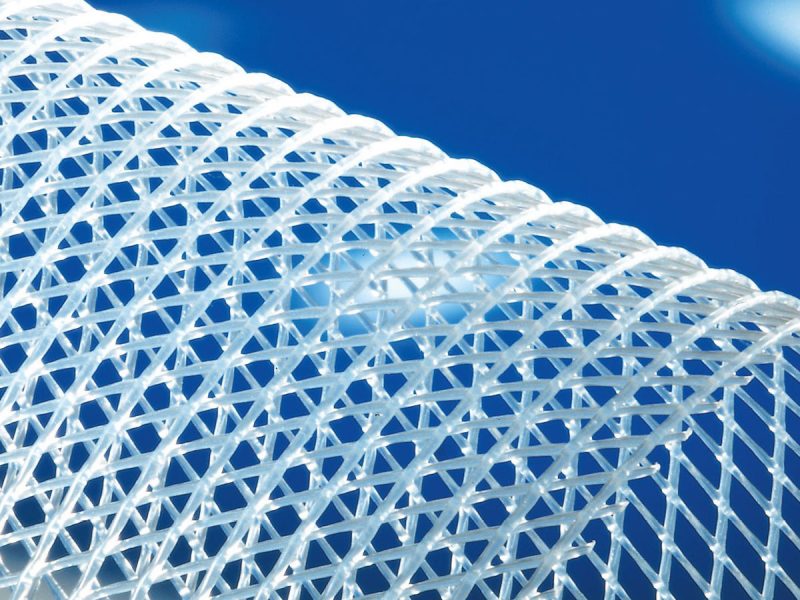
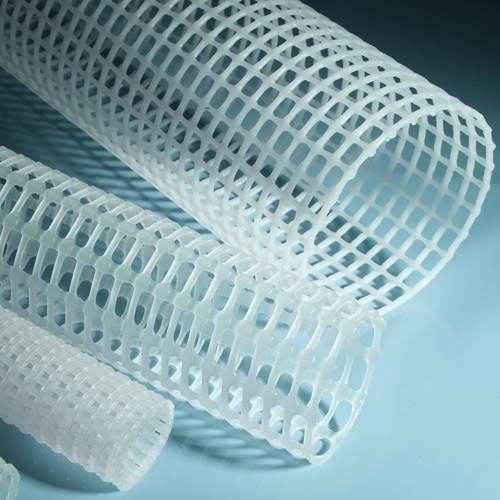
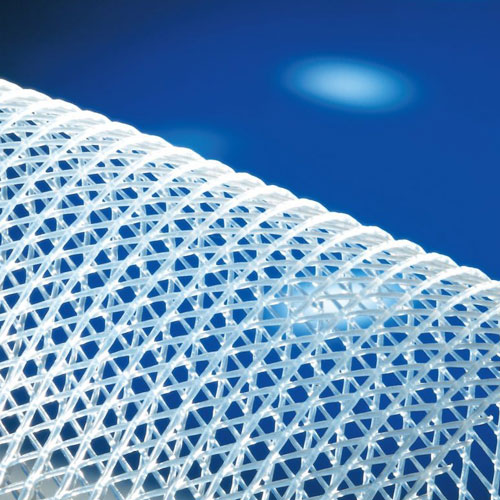
Through thermoplastic extrusion technology, TENAX designs and produces rigid mesh tubes, single or dual flat extruded nets, and elastic sleeves. These products are used in different fields which include industrial filter cartridges, air cabin, reverse osmosis (RO) filters, and pleated membranes.
Plastic components have become more and more important in the filtration market. In comparison to sheet metal, these items display many advantages. They have low weight, can be easily recycled and incinerated, are chemically inert, and suitable for ultra-sound (US) as well as low temperature welding.
The company aims at innovation to satisfy customers’ requirements and find new technological solutions for filters. Aside from our available product range, we constantly develop new products.

Raw materials
TENAX nets for industry are manufactured thanks to the extrusion of polyolefins and polyamides, which allow for a very good resistance against almost all chemicals and even micro-organisms such as spores, molds, and bacteria. These raw materials vary among them in some peculiar features.

hPP – Homopolymer polypropylene
- Specific weight: 0.9-0.915 g/cm3 (56.19-57.12 lb/ft3)
- Melting temperature: 162-168°C (323.6-334.4°F)
- Tensile strength: 34-37 MPa
- Young’s modulus: 1200-2000 Pa
- Yield elongation: 5-10%
- Break elongation: 500-700%
- Working temperature: +0°C – +90°C (32°F – 194°F)
- Max working temperature (short period): +100°C (212°F)
Light material, resistant to chemical substances (as salts, acids and strong alkalis) and with a high mechanical strength. It is used for bi-oriented (stretched) products. Suitable for direct food contact.
cPP – copolymer polypropylene
- Specific weight: 0.895-0.9 g/cm3 (54.62-56.19 lb/ft3)
- Melting temperature: 135-168°C (275-334.4°F)
- Tensile strength: 25-30 MPa
- Young’s modulus: 1000 Pa
- Yield elongation: 5-10%
- Break elongation: >500%
- Working temperature: -20°C – 70°C (68°F – 158°F)
- Max working temperature (short period): +80°C (176°F)
Slightly softer and more resistant to high temperature than the homopolymer but with similar mechanical features. Suitable for direct food contact.
PA6 (Nylon) -Polyamide 6
- Specific weight: 1.12-1.14 g/cm3 (69.91-71.16 lb/ft3)
- Melting temperature: 220-225°C (428-437°F)
- Tensile strength: 80 MPa (dry) –55 MPa (wet)
- Break elongation: 20-40% (dry) – 100% (wet)
- Working temperature: -40°C – 105°C (-40 – 221°F)
- Max working temperature (short period): 170°C (338°F)
It is an advanced polymer able to stand high temperatures and direct contact with oil, grease, fuel and other solvents. It shows a low friction coefficient and is resistant to abrasion, shocks and fatigue.
LDPE – Low-density polyethylene
- Specific weight: 0.915-0.920 g/cm3 (57.12-57.43 lb/ft3)
- Melting temperature: 105-118°C (221-244.4°F)
- Tensile strength: 10-25 MPa
- Young’s modulus: 150-300 Pa
- Yield elongation: –
- Break elongation: 550-600%
- Working temperature: -70°C – +40°C (-94°F – 104°F)
- Max working temperature (short period): 50°C (122°F)
Very soft material. It is mostly used for elastic sleeves for protecting goods. Can stand really low temperature.
HDPE – High-density polyethylene
- Specific weight: 0.94-0.96 g/cm3 (58.68-59.93 lb/ft3)
- Melting temperature: 126-135°C (258.8-275°F)
- Tensile strength: 25-35 MPa
- Young’s modulus: 800-1400 Pa
- Yield elongation: 10-12%
- Break elongation: >800%
- Working temperature: -40°C – +70°C (-40°F – 158°F)
- Max working temperature (short period): 75°C (167°F)
Outperforming chemical and good mechanical resistance. Within the polyethylene family it is the one which can stand at best high and low temperatures. It’s used for both extruded and stretched grids.